Article Plan⁚ Sitagliptin Phosphate in Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
Sitagliptin Phosphate⁚ Uses and Benefits
Sitagliptin phosphate‚ a medication commonly prescribed for type 2 diabetes‚ works by increasing the levels of incretin hormones in the body․ By doing so‚ it helps regulate blood sugar levels after meals․ One of the main benefits of sitagliptin is its ability to lower hemoglobin A1C levels‚ a marker of long-term blood sugar control․
Additionally‚ sitagliptin is known for its minimal risk of causing hypoglycemia‚ which is a common concern with some other diabetes medications․ This makes it a preferred choice for individuals who are at risk of low blood sugar episodes․ Moreover‚ sitagliptin is often well-tolerated with few adverse gastrointestinal effects compared to other antidiabetic drugs․
Furthermore‚ research has shown that sitagliptin may have cardiovascular benefits beyond just blood sugar control․ Studies suggest that it may help improve cardiovascular outcomes in patients with diabetes‚ making it a valuable treatment option for those with concomitant heart disease․
Understanding Sitagliptin Side Effects
While sitagliptin phosphate is generally well-tolerated‚ like any medication‚ it can potentially cause side effects․ Common side effects of sitagliptin include headache‚ respiratory tract infection‚ nasopharyngitis‚ and diarrhea․ These side effects are usually mild and temporary․
In rare cases‚ more severe side effects such as pancreatitis or allergic reactions may occur․ It is essential to seek immediate medical attention if experiencing symptoms like severe abdominal pain‚ persistent nausea or vomiting‚ rash‚ itching‚ or swelling of the face‚ lips‚ or throat․
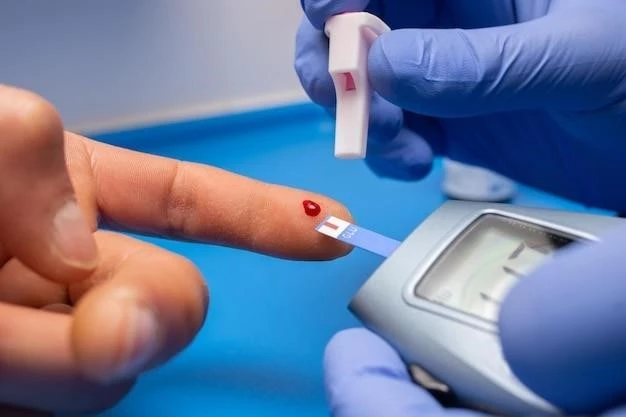
Patients should also be aware of the risk of hypoglycemia when taking sitagliptin‚ especially if used in combination with other antidiabetic medications․ It is crucial to monitor blood sugar levels regularly and be cautious when engaging in activities that can affect blood sugar levels․
Before starting sitagliptin or any new medication‚ individuals should discuss their medical history and any concerns with their healthcare provider to ensure the safest and most effective treatment plan․
Managing Headaches with Sitagliptin
Headaches are a common side effect reported by some individuals taking sitagliptin phosphate for type 2 diabetes․ While headaches can be bothersome‚ there are strategies to help manage them effectively․ It is essential to communicate any persistent or severe headaches to your healthcare provider․
One approach to managing headaches while on sitagliptin is to stay well-hydrated throughout the day․ Dehydration can sometimes trigger headaches‚ so ensuring adequate fluid intake may help reduce the frequency or intensity of headaches․ Additionally‚ practicing stress-relieving techniques such as deep breathing exercises or meditation can be beneficial․
If headaches persist or become severe‚ consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial to rule out any underlying issues․ Adjustments to the treatment plan‚ including potential changes in medication or dosage‚ may be considered to minimize headache occurrence․
Overall‚ proactive communication with your healthcare team‚ maintaining proper hydration‚ and incorporating stress management techniques can significantly aid in managing headaches associated with sitagliptin use․
Exploring Common Side Effects of Januvia
Januvia‚ a medication containing sitagliptin phosphate‚ is used to manage type 2 diabetes․ Like any medication‚ Januvia may cause certain side effects․ Common side effects of Januvia include upper respiratory tract infections‚ headaches‚ and gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and diarrhea․
In some cases‚ individuals taking Januvia may also experience mild allergic reactions like rash or hives․ Severe side effects such as pancreatitis or severe joint pain are rare but require immediate medical attention if they occur․
It is essential for individuals using Januvia to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and report any persistent or concerning side effects to their healthcare provider․ Adjustments to the treatment plan may be necessary to alleviate troublesome side effects while maintaining effective blood sugar control․
Understanding the potential side effects of Januvia and being proactive in discussing any symptoms with a healthcare professional can help ensure the safe and optimal management of type 2 diabetes while on this medication․
Sitagliptin and Metformin⁚ Side Effects Overview
When Sitagliptin‚ a DPP-4 inhibitor‚ is combined with Metformin‚ a biguanide‚ for the management of type 2 diabetes‚ it is important to be aware of potential side effects that may arise from this combination․ Common side effects of Sitagliptin and Metformin may include gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea‚ vomiting‚ diarrhea‚ or abdominal discomfort․
Some individuals may experience mild episodes of hypoglycemia when these medications are used together‚ particularly if the dosage is not adjusted appropriately․ Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial to prevent and manage hypoglycemic events effectively․
In rare cases‚ serious side effects like lactic acidosis‚ a rare but potentially severe condition‚ can occur with Metformin use․ Symptoms of lactic acidosis include muscle cramps‚ weakness‚ trouble breathing‚ dizziness‚ and unusual fatigue and should be reported to a healthcare provider immediately․
It is essential for individuals prescribed Sitagliptin and Metformin to discuss any side effects experienced with their healthcare provider promptly․ By maintaining open communication and monitoring for signs of both common and rare side effects‚ the healthcare team can adjust the treatment plan as needed to ensure optimal diabetes management․
Important Information on Sitagliptin for Type 2 Diabetes
Sitagliptin is a commonly prescribed medication for the management of type 2 diabetes․ It belongs to the class of DPP-4 inhibitors and works by regulating blood sugar levels after meals․ Individuals with type 2 diabetes can benefit from the use of sitagliptin in conjunction with diet and exercise to improve glycemic control․
Before initiating sitagliptin therapy‚ it is crucial for healthcare providers to assess the patient’s medical history‚ including any comorbid conditions and current medications‚ to ensure the safety and efficacy of treatment․ Patients should also be educated on the proper use of sitagliptin‚ including dosing instructions and potential side effects․
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential while taking sitagliptin to gauge the medication’s effectiveness and make any necessary adjustments․ Individuals should also be aware of the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia and how to respond to these conditions appropriately․
Overall‚ sitagliptin can be a valuable addition to the treatment regimen for type 2 diabetes‚ offering benefits in blood sugar management with a relatively low risk of hypoglycemia․ By working closely with their healthcare team‚ individuals can optimize their diabetes care and enhance their overall quality of life․
