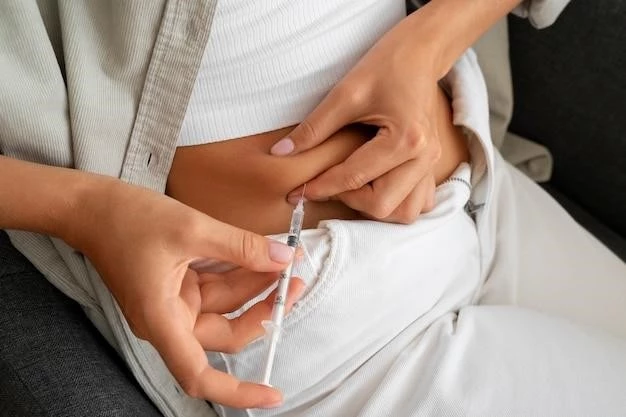
Proper Administration Techniques
When administering progesterone injections, ensure clean hands and sanitized injection site. Follow correct dosage and injection method as instructed by a healthcare provider. Rotate injection sites to minimize tissue irritation. Use a new needle for each injection to prevent infection.
Guidelines for Safe Administration
Follow proper storage instructions for progesterone injections. Keep out of reach of children and store at room temperature. Dispose of used needles in a sharps container. Seek medical assistance if any signs of infection or allergic reaction occur; Adhere to the recommended injection schedule provided by your healthcare professional.
Common Uses of Antiprogestins
Antiprogestins are used in the treatment of conditions like endometriosis, uterine fibroids, and certain types of cancer. They can also be prescribed for emergency contraception and to induce labor in specific situations. Additionally, antiprogestins may be used in hormone replacement therapy.
Potential Side Effects
Common side effects of antiprogestins include nausea, breast tenderness, changes in menstrual flow, and headaches. In some cases, they may lead to mood changes, weight gain, or skin reactions. Serious side effects are rare but may include blood clots or allergic reactions. Consult a healthcare provider if experiencing severe side effects.
Common Side Effects
Common side effects of progesterone vaginal administration may include vaginal discharge, irritation, itching, or changes in menstrual bleeding patterns. These effects are typically mild and transient. It is important to monitor and report any persistent or bothersome side effects to a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Warning Signs
Be alert for warning signs of serious side effects from progesterone vaginal use, including severe vaginal irritation, allergic reactions (such as rash or difficulty breathing), or symptoms of a blood clot such as sudden leg pain or chest pain. Contact a healthcare provider immediately if any of these warning signs occur.
Benefits of Progesterone for PMS
Progesterone can help alleviate symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) such as mood swings, bloating, and breast tenderness. It may also regulate menstrual cycles and reduce cramping. Discuss with a healthcare provider to determine if progesterone is a suitable option for managing PMS symptoms.

Considerations Before Use
Prior to using progesterone for PMS, consider factors such as medical history, current medications, and underlying conditions. Discuss any potential risks or interactions with a healthcare provider. It’s essential to follow recommended dosage and schedule to maximize benefits and minimize any adverse effects. Regularly monitor PMS symptoms and report any concerning changes to your healthcare provider.
Benefits of Combined Therapy
Combining progesterone and estrogen therapy can help alleviate menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness. It may also reduce the risk of osteoporosis and protect against certain cancers. Consult a healthcare provider to discuss the potential benefits of this combined approach for managing menopause.
Risks to Consider
When using progesterone and estrogen therapy, risks may include an increased risk of blood clots, stroke, breast cancer, or heart disease. It’s crucial to discuss individual health risks, monitor for any adverse effects, and follow up regularly with a healthcare provider. Understanding and weighing these risks is essential for making informed decisions about hormone therapy.
Common Menopausal Symptoms
Common menopausal symptoms include hot flashes, night sweats, mood changes, vaginal dryness, and sleep disturbances. Women may also experience changes in libido, weight fluctuations, and cognitive issues. It’s essential to recognize these symptoms and seek guidance from a healthcare provider for appropriate management.
Management Strategies
Management of menopausal symptoms may involve lifestyle changes, hormone therapy, or alternative therapies like acupuncture or herbal supplements. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management, and adequate sleep can also help alleviate symptoms. Consult with a healthcare provider to create a tailored management plan that addresses individual needs and preferences.