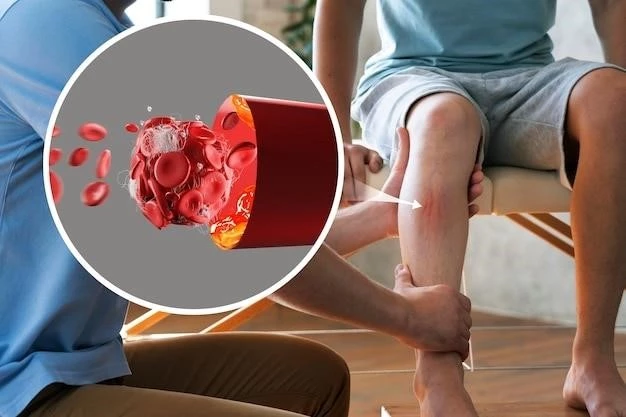
Article Plan⁚ Probalan in Gout Treatment
Probalan⁚ Benefits and Uses
Understanding Probenecid Side Effects
How Probalan Helps in Gout Treatment
Probenecid Drug Interactions to be Aware Of
Tips for Managing Probenecid Side Effects
Exploring the Mechanism of Probalan in Treating Gout
Probalan⁚ Benefits and Uses
Probalan, also known as Probenecid, is a medication primarily used to treat gout by increasing uric acid excretion in the urine. It is beneficial in preventing gout attacks and reducing the frequency of flare-ups. Additionally, it can be used in combination with certain antibiotics to enhance their effectiveness by increasing their concentration in the blood.
Probalan is also prescribed to manage certain types of kidney stones by preventing the formation of uric acid stones. Its benefits extend to prolonging the effects of certain medications by slowing down their elimination from the body. This medication is essential for individuals who struggle with high levels of uric acid in their blood, which can lead to conditions like gout and kidney stones.
Understanding the benefits and uses of Probalan is crucial for healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding its prescription for patients with gout or other related conditions. By recognizing its role in managing uric acid levels and preventing associated complications, Probalan stands as a valuable treatment option in the realm of gout therapy and related disorders.
Understanding Probenecid Side Effects
As with any medication, Probenecid may cause side effects that individuals should be aware of. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, and loss of appetite; More severe side effects may include blood in urine, difficulty breathing, chest pain, and unusual bleeding or bruising.
It is important for patients using Probenecid to monitor their symptoms closely and report any adverse effects to their healthcare provider promptly. Some individuals may experience allergic reactions such as rash, itching, or swelling, which require immediate medical attention. Understanding the potential side effects of Probenecid is essential for maintaining patient safety and well-being.
Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in educating patients about the side effects of Probenecid, emphasizing the importance of adherence to prescribed dosages and regular monitoring during treatment. By proactively addressing and managing potential side effects, healthcare providers can optimize the therapeutic benefits of Probenecid while minimizing risks to patient health.
How Probalan Helps in Gout Treatment
Probalan plays a vital role in the treatment of gout by promoting the excretion of uric acid from the body. High levels of uric acid can lead to the formation of urate crystals in joints, causing inflammation and intense pain characteristic of gout attacks. By enhancing the elimination of uric acid through the urine, Probalan helps reduce the concentration of urate crystals in the joints, thereby decreasing the frequency and severity of gout flares.
Furthermore, Probalan can be used in combination with other medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or colchicine, to provide comprehensive gout management. This multi-faceted approach helps address both the symptoms and underlying causes of gout, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Healthcare professionals often consider Probalan as a valuable addition to the treatment regimen for individuals with gout, especially in cases where dietary changes and lifestyle modifications are insufficient to control the condition. By understanding how Probalan facilitates uric acid elimination and complements other gout therapies, healthcare providers can deliver a more comprehensive and effective treatment strategy for patients suffering from this debilitating arthritic condition.
Probenecid Drug Interactions to be Aware Of
When prescribing Probenecid, healthcare providers must be mindful of potential drug interactions that can affect its effectiveness or lead to adverse effects. Probenecid interacts with various medications, including antibiotics like penicillin and cephalosporins, as well as certain nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as indomethacin;
Combining Probenecid with certain antibiotics can increase their levels in the blood, enhancing their therapeutic effects. However, interactions with NSAIDs may impact kidney function and require dosage adjustments to prevent kidney damage. Additionally, Probenecid may alter the metabolism of medications like methotrexate and theophylline, affecting their clearance from the body.
Patient medication profiles should be thoroughly reviewed to identify potential interactions before initiating Probenecid therapy. Close monitoring of patients receiving Probenecid in combination with other medications is essential to ensure treatment efficacy and safety. Healthcare providers must remain vigilant in managing drug interactions to optimize patient outcomes and prevent any potential complications.
Tips for Managing Probenecid Side Effects
Managing side effects of Probenecid is crucial for optimizing patient adherence and treatment outcomes. Patients should follow these tips to minimize and address potential adverse reactions⁚
- Stay hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water daily to help prevent kidney stones and maintain kidney function.
- Monitor for signs of allergic reactions like rash, hives, or swelling, and seek immediate medical attention if any occur.
- Report any unusual symptoms or side effects to your healthcare provider promptly for evaluation and management.
- Avoid alcohol consumption as it may exacerbate certain side effects like dizziness or gastrointestinal upset.
- Follow the prescribed dosage and schedule meticulously to ensure optimal effectiveness and minimize the risk of side effects.
- Consult your healthcare provider before taking any new medications or supplements to prevent potential interactions with Probenecid.
- Engage in open communication with your healthcare team to address any concerns or questions about Probenecid therapy.
By adhering to these tips and maintaining proactive communication with healthcare providers, patients can effectively manage side effects associated with Probenecid therapy, enhancing treatment efficacy and safety.
Exploring the Mechanism of Probalan in Treating Gout
Probalan exerts its therapeutic effects in treating gout by acting as a uricosuric agent, increasing the excretion of uric acid in the kidneys. This process reduces the serum urate concentrations in the blood, preventing the precipitation of urate crystals in joints which is the hallmark of gout.
By inhibiting the reabsorption of uric acid in the renal tubules and promoting its elimination through urine, Probalan helps lower uric acid levels in the body. This mechanism of action not only alleviates acute gout symptoms but also prevents long-term complications such as joint damage and deformity associated with chronic gout.
Furthermore, Probalan aids in enhancing the efficacy of certain antibiotics by increasing their concentration in the bloodstream through competitive inhibition of renal tubular secretion; This dual functionality of Probalan demonstrates its versatility in gout treatment and its potential to synergize with other medications for improved patient outcomes.
Understanding the intricate mechanism of Probalan in treating gout provides healthcare providers with insights into its therapeutic benefits and aids in optimizing its use in clinical practice. By exploring the pharmacology of Probalan, healthcare professionals can tailor treatment regimens to effectively manage gout and its associated complications.