Article Plan⁚ Uses and Benefits of Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen therapy plays a critical role in various medical treatments by increasing oxygen levels in the blood, aiding in the management of respiratory conditions, improving overall health, and enhancing quality of life for individuals with chronic respiratory diseases.
Understanding Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen therapy is a medical intervention that involves the administration of oxygen to individuals with respiratory disorders or conditions that result in low blood oxygen levels. It is delivered through various devices like nasal cannulas, face masks, and ventilators. The primary goal of oxygen therapy is to increase the oxygen levels in the blood to improve tissue oxygenation, relieve symptoms of hypoxia, reduce the workload on the heart, and enhance overall well-being.
There are different types of oxygen therapy, including long-term oxygen therapy (LTOT) for chronic conditions like COPD, and short-term oxygen therapy for acute conditions such as respiratory failure. Oxygen therapy is prescribed by healthcare professionals based on individual needs and oxygen saturation levels. Monitoring is crucial to ensure the proper dosage and effectiveness of the therapy without causing oxygen toxicity.
Understanding the principles of oxygen therapy, the equipment used, and the importance of compliance are essential for patients and caregivers. Proper education on oxygen safety, storage, and maintenance of equipment is vital to ensure the effectiveness and safety of oxygen therapy. Overall, a comprehensive understanding of oxygen therapy is crucial for optimizing its benefits and improving the quality of life for individuals with respiratory conditions.
Oxygen Therapy Side Effects⁚ What to Know
While oxygen therapy is generally safe and beneficial, it can have potential side effects if not used correctly. Common side effects include nasal dryness, nosebleeds, fatigue, and headaches. In some cases, oxygen therapy can lead to oxygen toxicity, a condition that can cause lung damage due to prolonged exposure to high levels of oxygen.
Patients receiving oxygen therapy should be monitored closely for signs of oxygen toxicity, such as coughing, chest pain, shortness of breath, and changes in the color of the lips or fingernails. It is crucial for healthcare providers to adjust the oxygen flow rate based on the patient’s oxygen saturation levels to prevent toxicity.
Properly maintaining and cleaning oxygen equipment, following prescribed oxygen flow rates, and avoiding smoking or open flames near oxygen sources can help minimize the risk of side effects. Patients should also be educated on the importance of using oxygen therapy as prescribed and seeking medical advice if they experience any unusual symptoms.
Understanding the potential side effects of oxygen therapy and taking appropriate precautions can help ensure the safe and effective use of supplemental oxygen to improve respiratory function and enhance overall well-being for individuals with respiratory conditions.
Information on Drug Side Effects
When considering the use of medications alongside oxygen therapy, it is crucial to be aware of potential drug interactions and side effects. Certain medications may interact with oxygen therapy, impacting its effectiveness or causing adverse reactions. Patients and healthcare providers must understand the possible effects of combining oxygen therapy with specific drugs.
Common drug side effects that may occur in conjunction with oxygen therapy include respiratory depression, drowsiness, dizziness, or changes in blood pressure. It is essential for healthcare professionals to carefully monitor patients receiving both oxygen therapy and medications to prevent any negative outcomes.
Patient education on drug interactions, potential side effects, and the importance of medication adherence is paramount to ensure the safe and successful management of respiratory conditions. Collaborative efforts between healthcare providers, pharmacists, and patients are necessary to minimize risks and optimize treatment outcomes when utilizing medications alongside oxygen therapy.
By staying informed about potential drug interactions and side effects, healthcare teams can tailor treatment plans to each patient’s specific needs, promoting therapeutic efficacy while mitigating any associated risks.
Oxygen Therapy in Clinical Settings
In clinical settings, oxygen therapy is a vital intervention used to treat various medical conditions related to inadequate oxygen levels in the blood. Healthcare professionals carefully assess patients’ oxygen needs through pulse oximetry and blood gas analysis to determine the appropriate oxygen therapy delivery method and flow rate.
Oxygen therapy in clinical settings is commonly administered using oxygen cylinders, concentrators, or ventilators, tailored to meet the specific requirements of each patient. Proper monitoring of oxygen saturation levels and the patient’s response to therapy is essential to adjust oxygen delivery as needed and prevent over or under oxygenation.
Clinical staff, including doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists, are trained to manage oxygen therapy effectively, ensuring patient safety and treatment efficacy. They work collaboratively to monitor patients, address any complications or side effects, and optimize oxygen therapy outcomes. Education on oxygen therapy protocols, equipment operation, and emergency procedures is crucial for healthcare providers working in clinical settings.
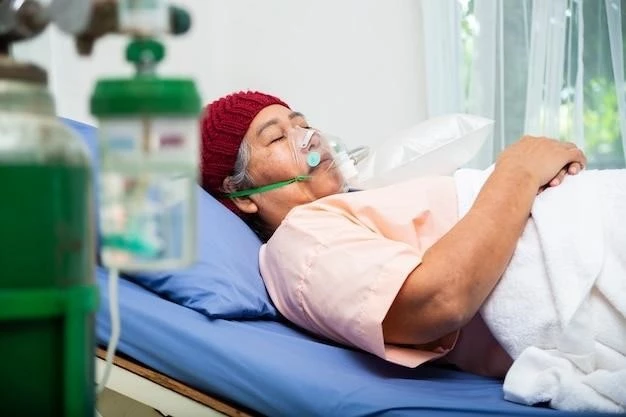
By implementing standardized protocols and guidelines for oxygen therapy administration, clinical teams can deliver high-quality care, improve patient outcomes, and enhance the overall quality of medical treatment. Oxygen therapy in clinical settings remains a cornerstone of respiratory care, supporting patients with acute or chronic respiratory conditions to breathe more comfortably and improve their health status.
Risks and Benefits of Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen therapy offers a range of benefits for patients with respiratory conditions, including improved oxygen levels in the blood, enhanced tissue oxygenation, decreased shortness of breath, and increased energy levels. By delivering supplemental oxygen, therapy can aid in managing various respiratory illnesses, supporting better lung function and overall well-being.
However, like any medical intervention, oxygen therapy also carries certain risks. Potential risks of oxygen therapy include oxygen toxicity, which can lead to lung damage, especially with prolonged exposure to high levels of oxygen; Other risks may include fire hazards associated with oxygen use, nasal irritation, and the development of oxygen dependency in some cases.
Healthcare providers carefully evaluate the benefits versus risks of oxygen therapy for each patient, considering factors such as the underlying condition, oxygen saturation levels, and the need for supplemental oxygen. Monitoring patients closely during therapy helps to mitigate potential risks and ensure optimal benefits from treatment.
Overall, the benefits of oxygen therapy in improving respiratory function and enhancing quality of life often outweigh the associated risks when used appropriately and under proper medical supervision. By weighing these factors and individualizing treatment plans, healthcare professionals strive to provide effective oxygen therapy that maximizes benefits while minimizing potential adverse effects.
